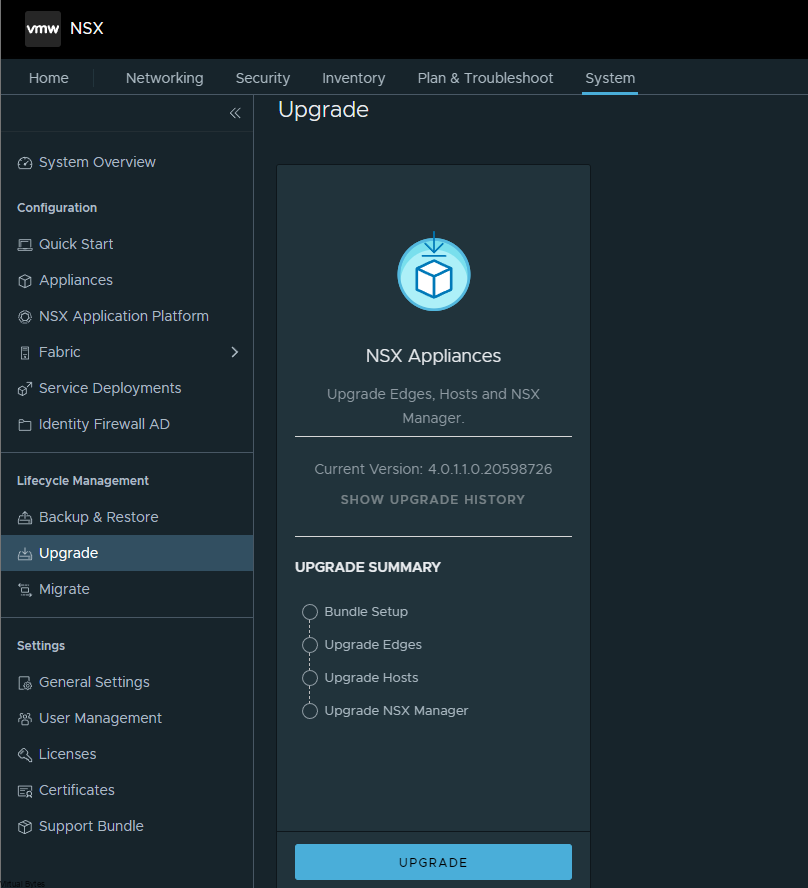
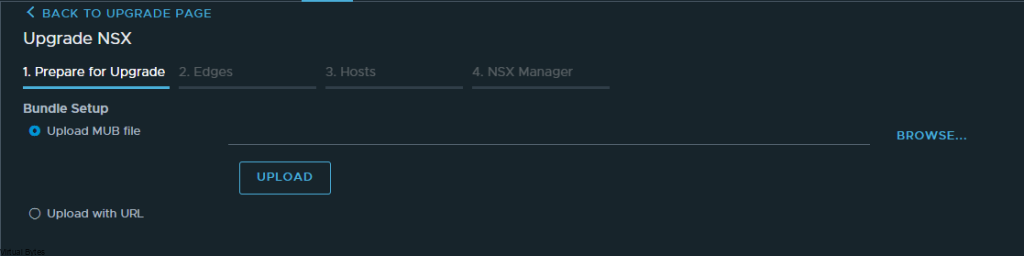
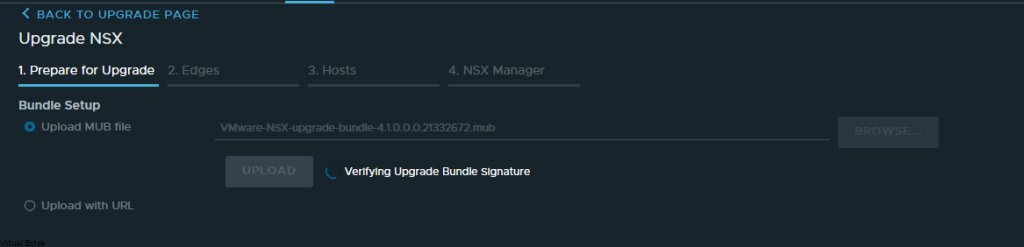
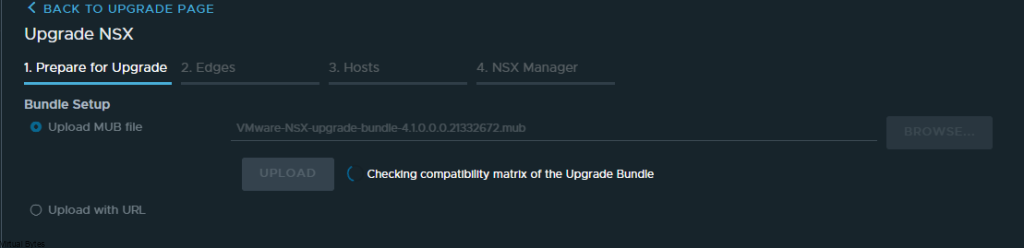
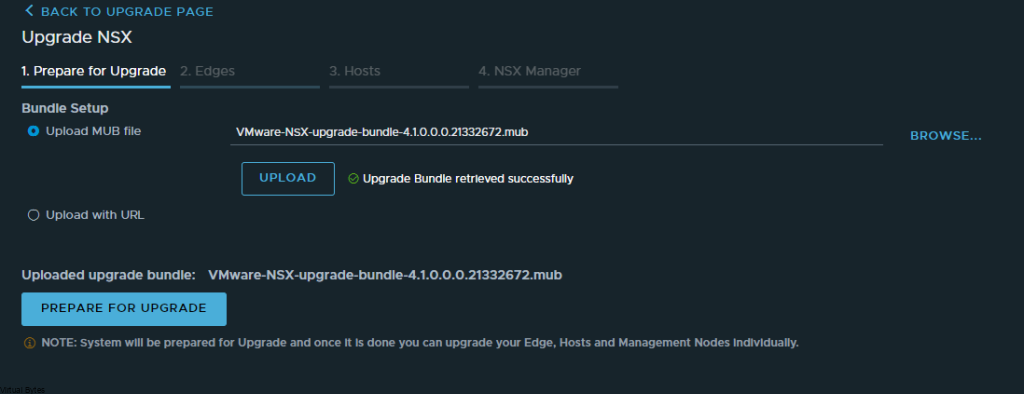
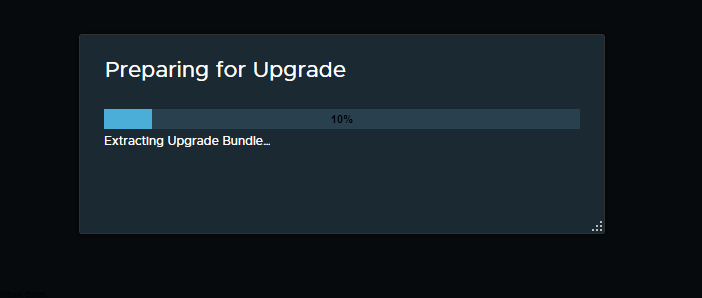
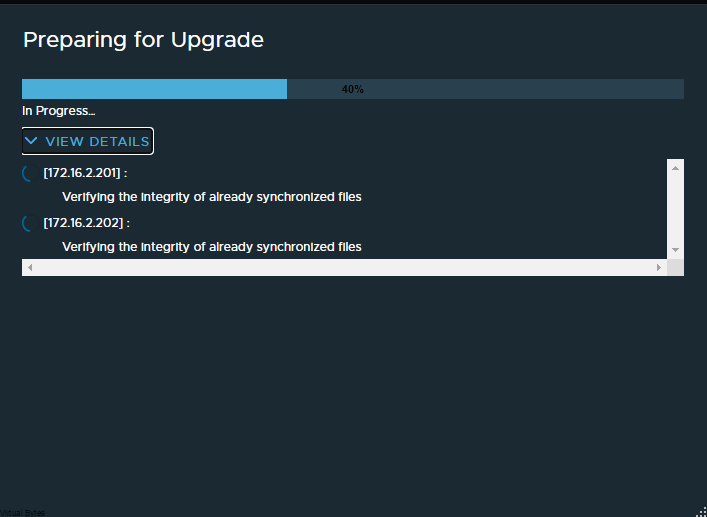
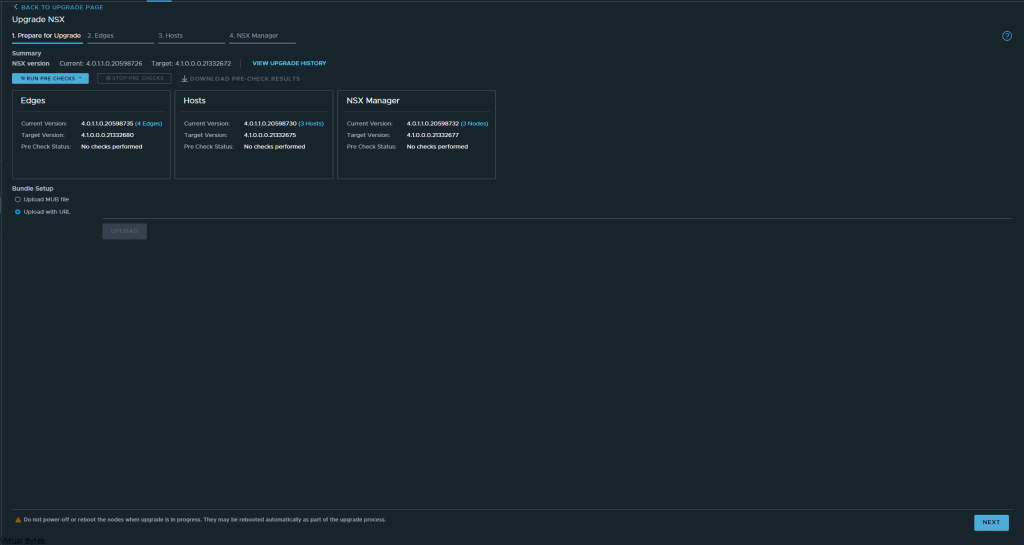
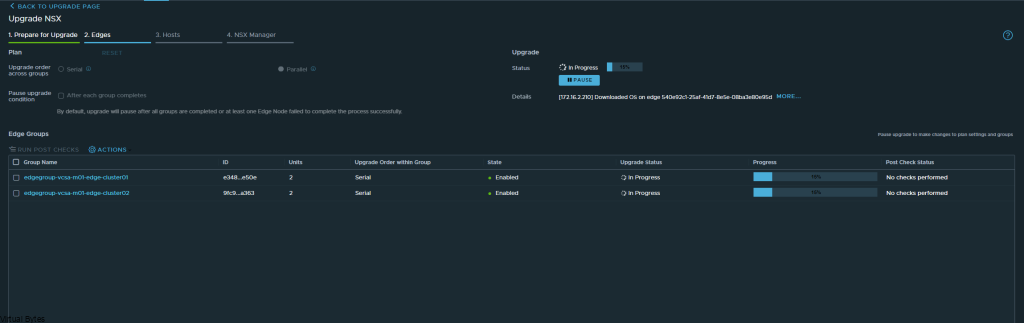
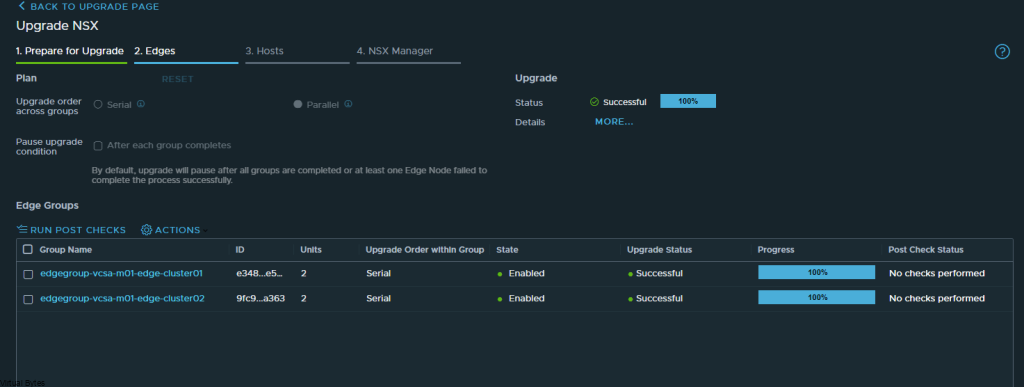
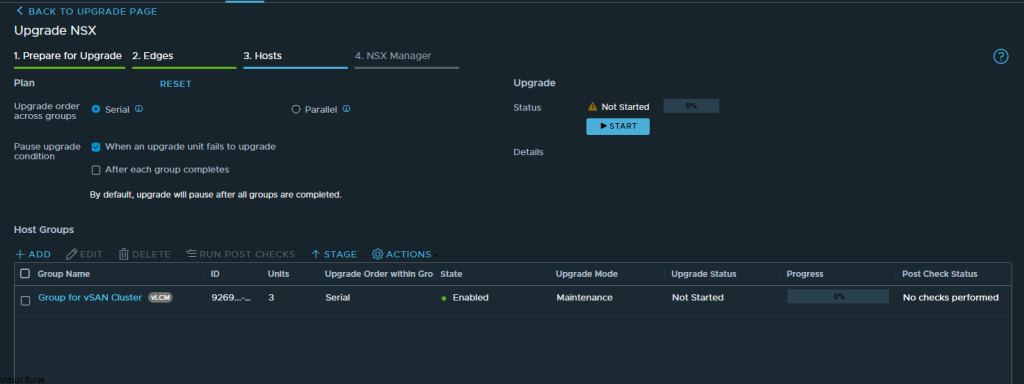
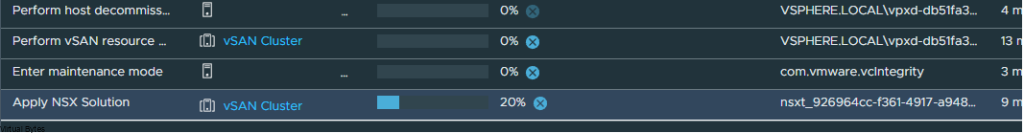
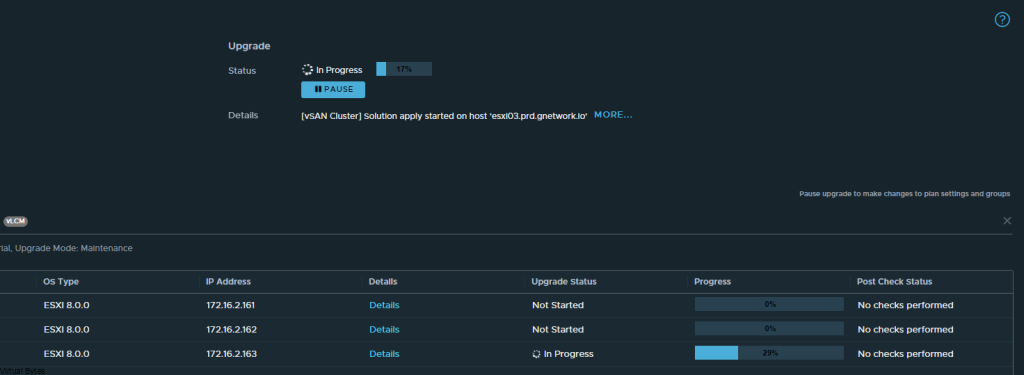
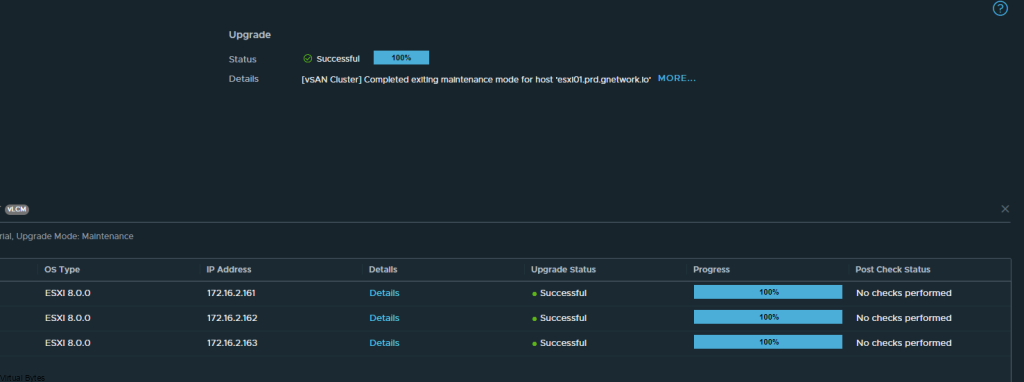
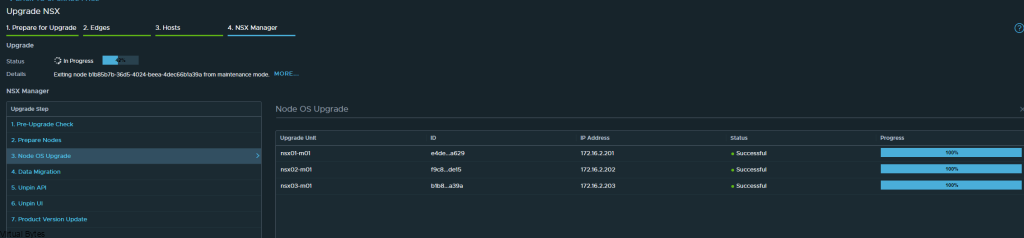
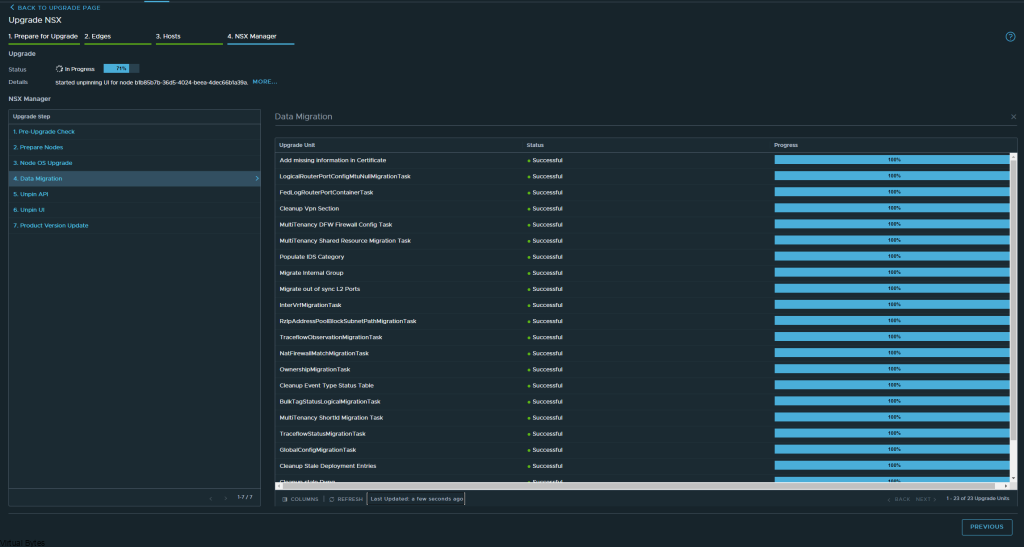
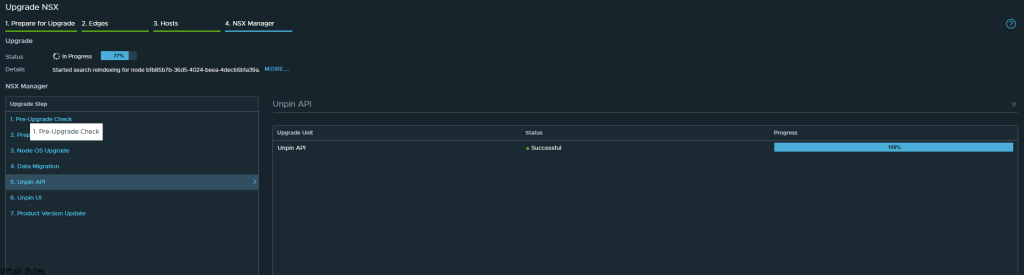
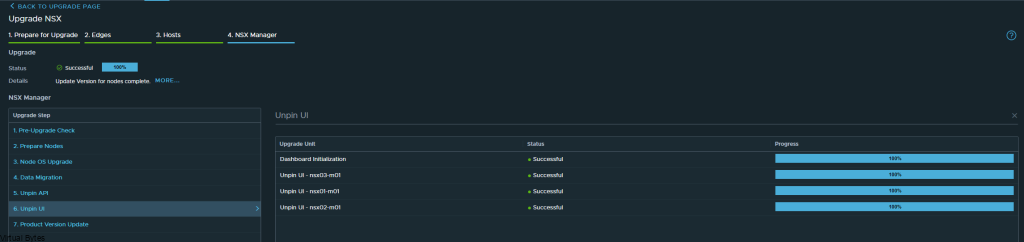
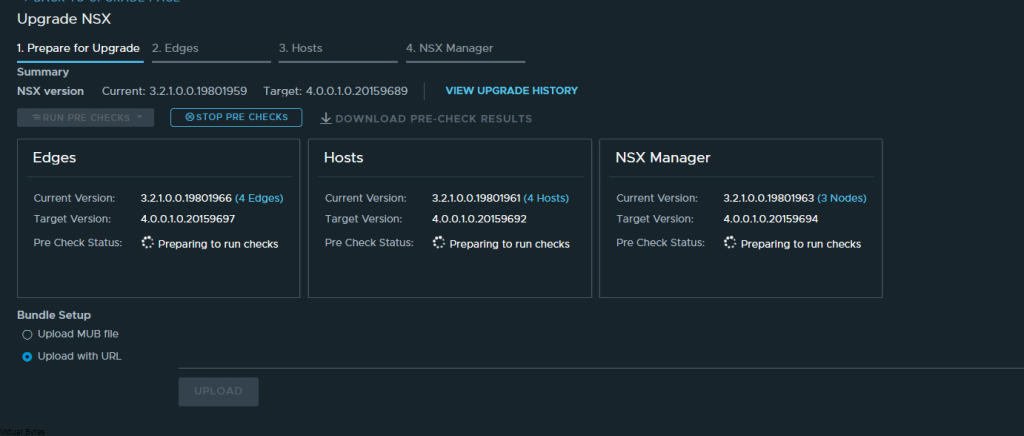
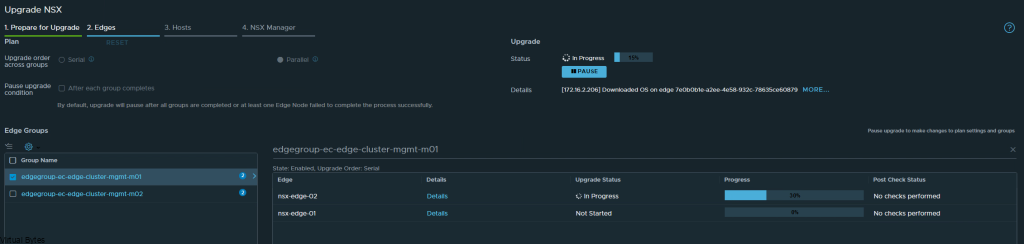
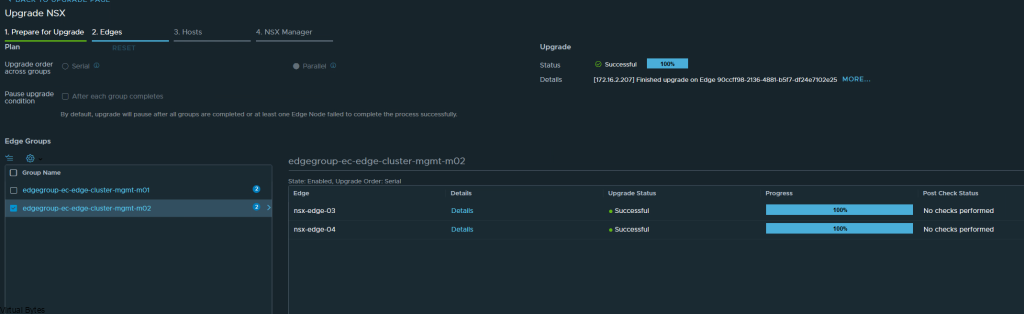
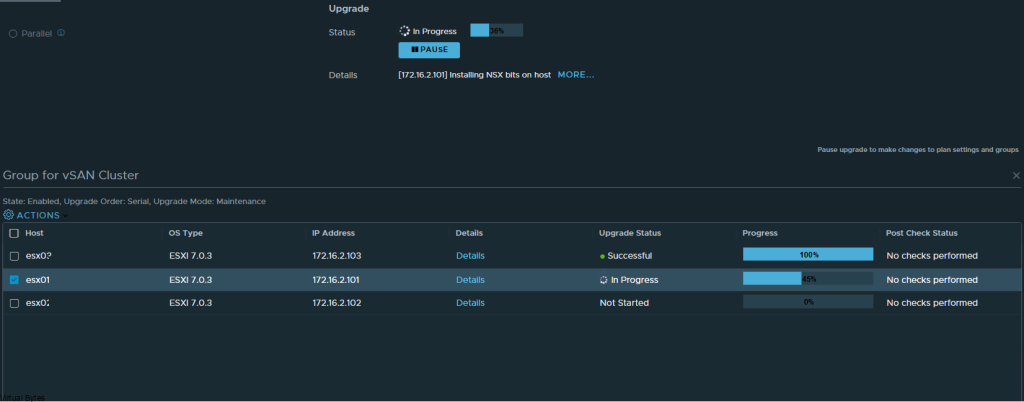
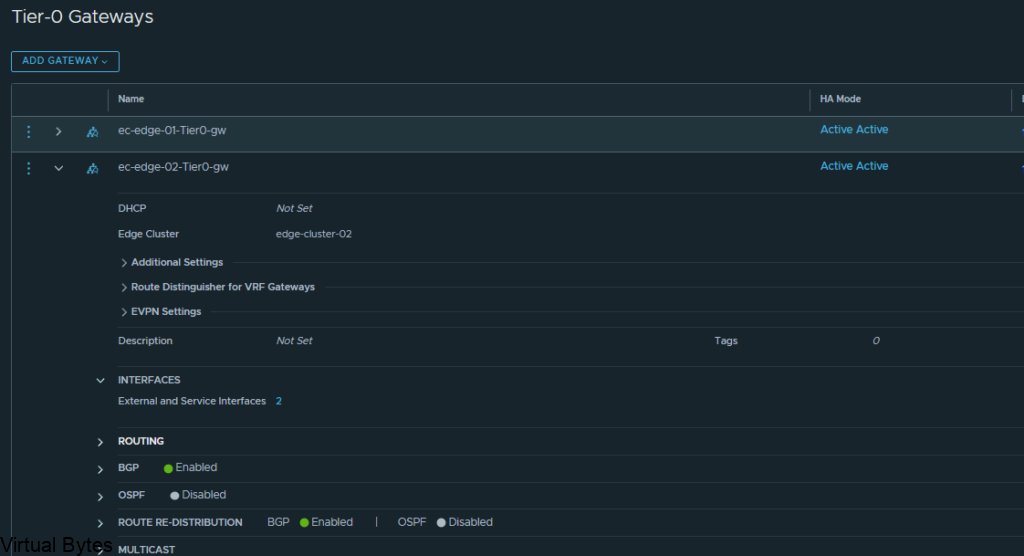
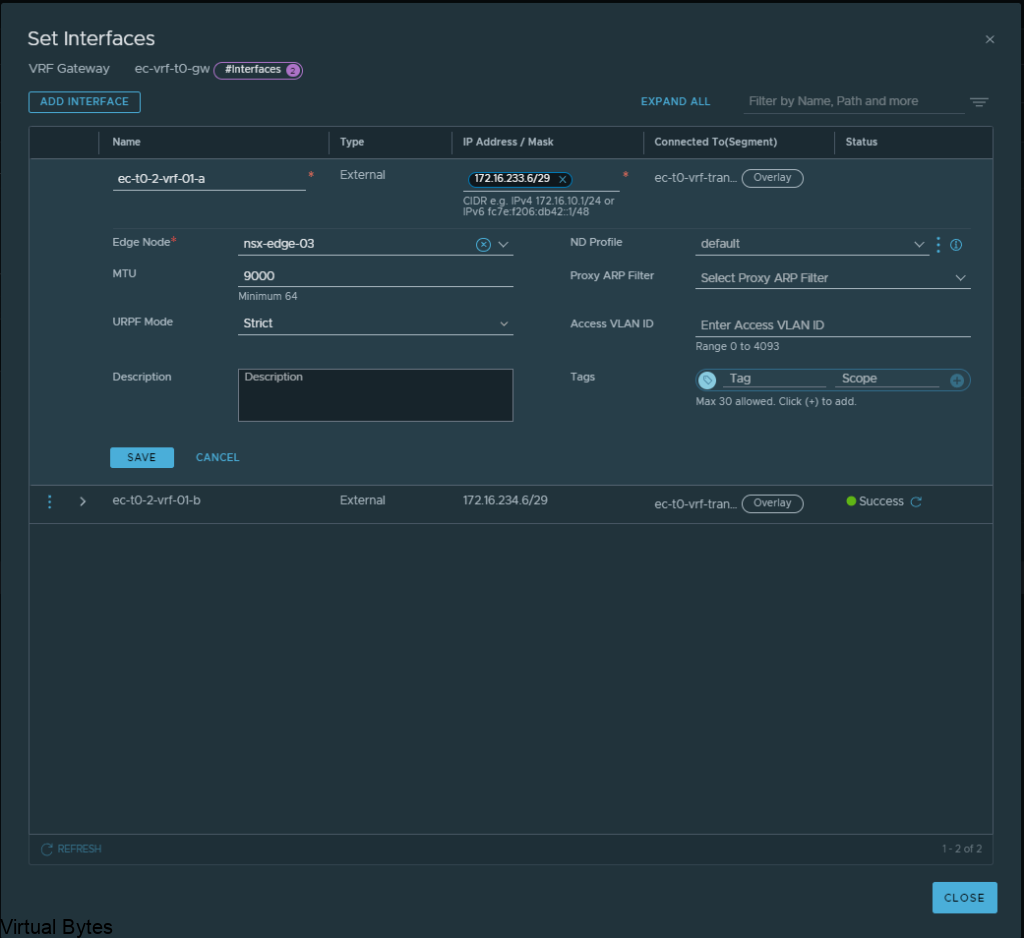
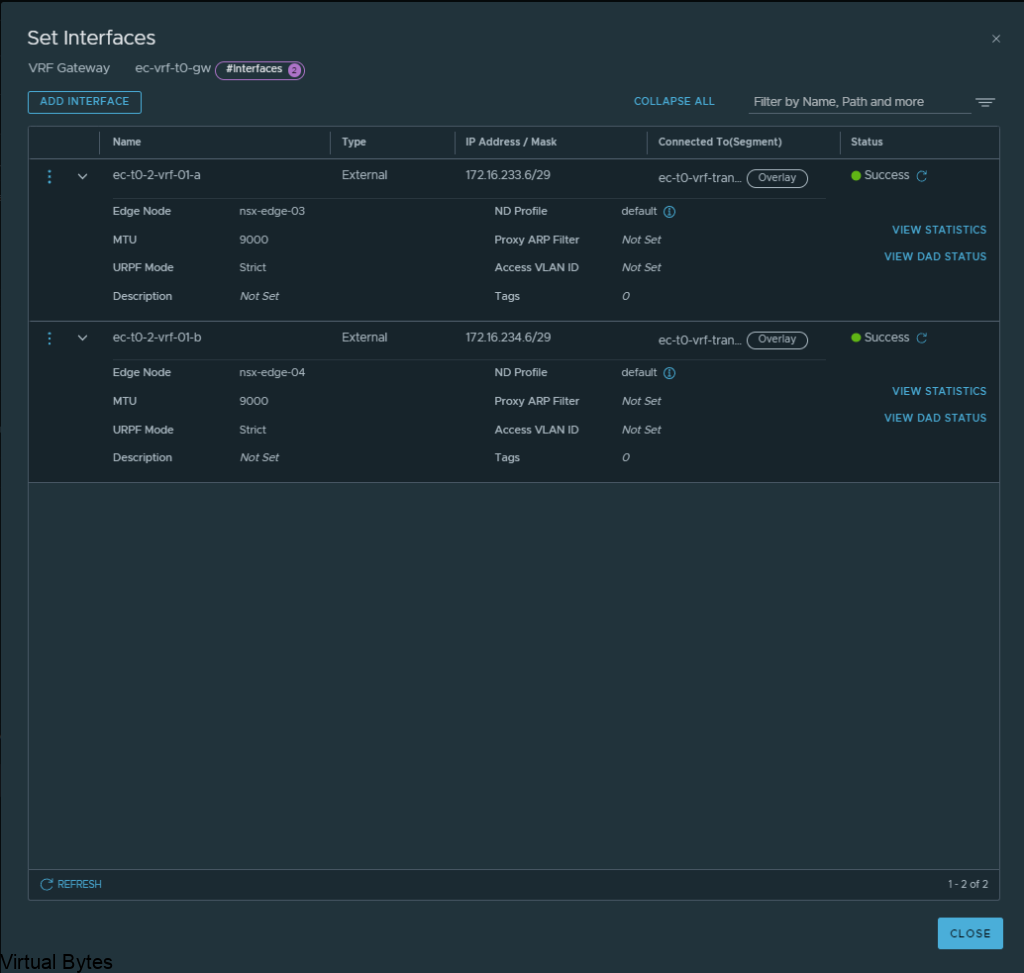
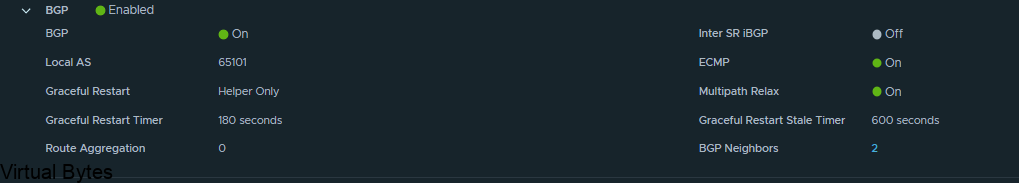
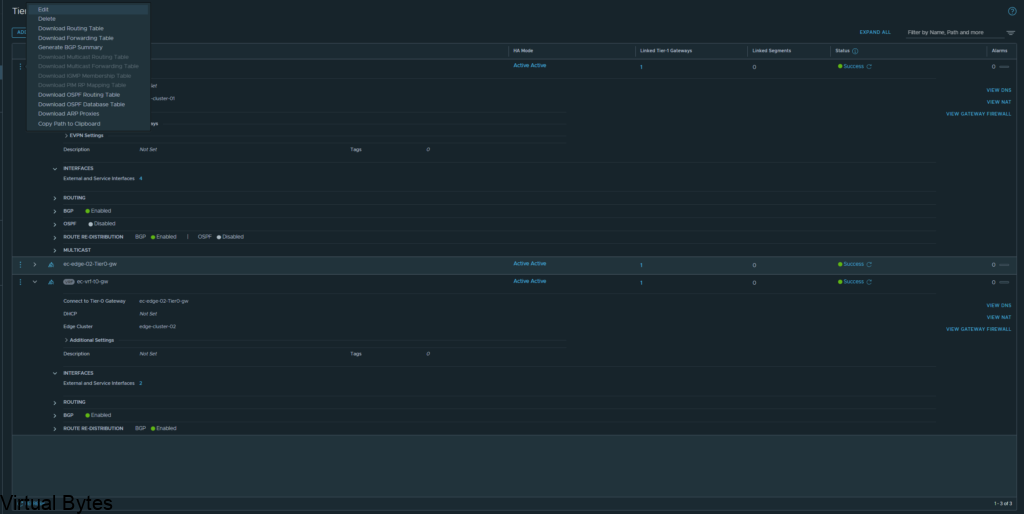
If you’ve recently upgraded your NSX environment and noticed a spike in disk usage for the repository partition, you’re not alone. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the reasons behind this increase and provide some tips on how to manage and optimize your disk space. We’ll discuss common causes for the surge in disk usage post-upgrade, and explore some best practices for keeping your NSX environment running smoothly.
VMware Cloud Foundation (SDDC Manager) Password Lookup Utility
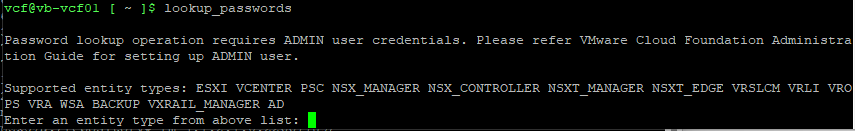
Next, we will need to SSH into the NSX Managers, if you are running NSX within VMware Cloud Foundation, you will need to run the VCF Lookup Password Utility within the SDDC Manager and login via remote console in vSphere to enable SSH services
To Start SSH Service on NSX Manager –
start service sshTo Enable SSH Service on reboot –
set service start-on-boot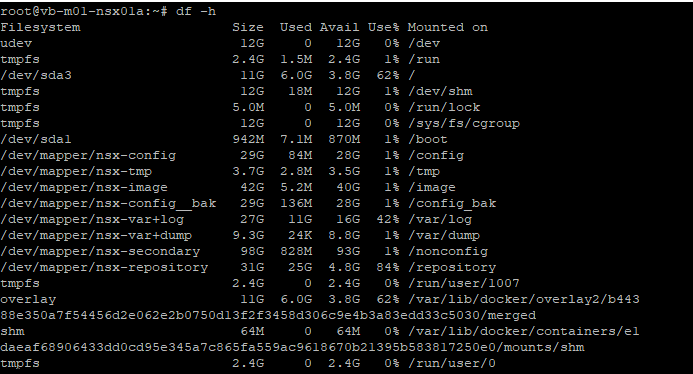
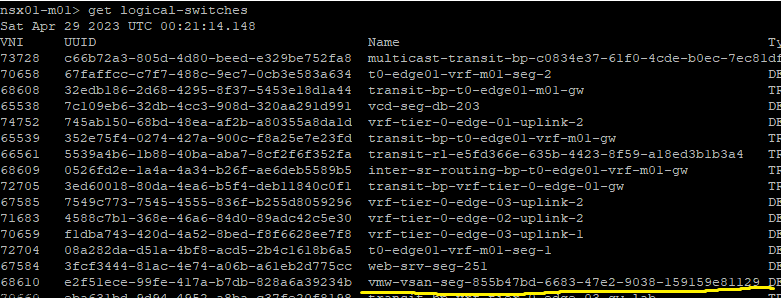
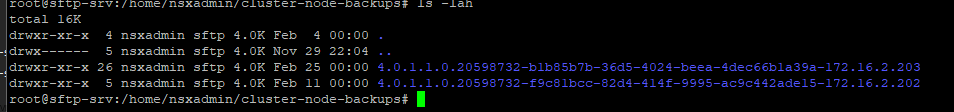
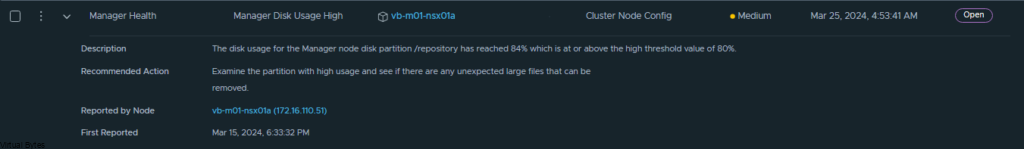
There is the 84% Usage of the repository partition, this partition holds all the previous patches and upgrades of NSX.
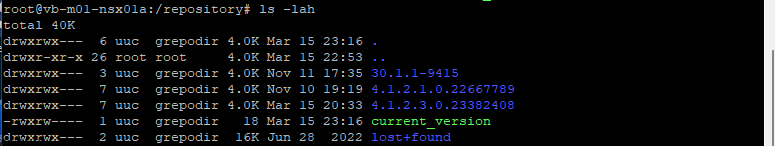
Now we delete the old folders, I also had old version of NSX Advanced Load Balancer which I cleaned up as well.
Example –
rm -rf 4.1.2.1.0.22667789/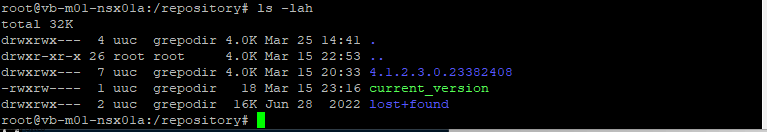
There we go! No more alarms for high disk usage.
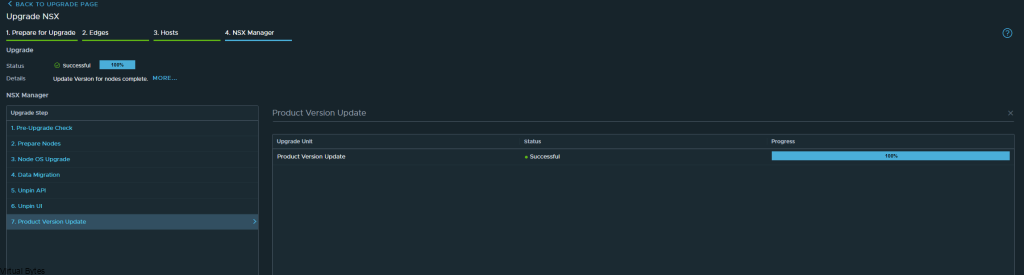
After a upgrade of your VMware NSX environment, it is always good to clean up the bundles and old binaries to prevent high disk usage and prevent and issue with your NSX Managers.