Tonight’s multi-post is about VMware Cloud Director 10.4.x and Terraform!
With Terraform there are endless possibilities, creating a virtual data center and being able to tailor to your liking and keeping it in an automated deployment. In this multi-part blog post we will get into VCD and Terraform Infrastructure as Code automation. If you would like to see what we did in Part 1, here is the previous post – VMware Cloud Director 10.4.X & Terraform Automation Part 1
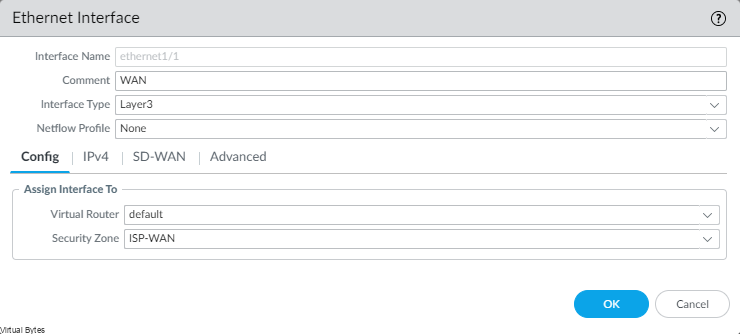
What You will Need:
- A Linux VM to execute Terraform from
- Latest Terraform Provider (I am using beta 3.9.0-beta.2 )
- Gitlab / Code Repo (Optional to store your code)
- VMware Cloud Director with NSX-T Integrated already
- Local Account with Provider Permissions on VCD (mine is terraform)
Lets Begin!
First part we will add on to our existing Terraform automation which we have continued in Part 1 of this multi-part blog. Below is the provider information for reference.
terraform {
required_providers {
vcd = {
source = "vmware/vcd"
version = "3.9.0-beta.2"
}
}
}
provider "vcd" {
url = "https://cloud.virtualbytes.io/api"
org = "system"
user = "terraform"
password = "VMware1!"
auth_type = "integrated"
max_retry_timeout = 60
allow_unverified_ssl = true
}Next, we will add Data Center Groups to our terraform template, what we are doing here is Creating the virtual data center group to span multiple organizations, if need be, but for this demonstration – I am using a DCG for Distributed Firewall purposes.
#### Create VDC Org Group
resource "vcd_vdc_group" "demo-vdc-group" {
depends_on = [vcd_org_vdc.demo-org-10]
org = "demo-org-10"
name = "demo-vdc-group"
description = "Demo Data Center Group"
starting_vdc_id = vcd_org_vdc.demo-org-10.id
participating_vdc_ids = [vcd_org_vdc.demo-org-10.id]
dfw_enabled = true
default_policy_status = true
}The next code snippet – here we will set and configure the Data Center Group firewall from an Internal to Internal and Drop to Any to Any and Allow. Configuration where by default it keeps Internal DFW rule.
##### DFW VDC Group to Any-Any-Allow
resource "vcd_nsxt_distributed_firewall" "lab-03-pro-dfw" {
depends_on = [vcd_org_vdc.demo-org-10]
org = "demo-org-10"
vdc_group_id = vcd_vdc_group.demo-vdc-group.id
rule {
name = "Default_VdcGroup_demo-vdc-group"
direction = "IN_OUT"
ip_protocol = "IPV4"
source_ids = [vcd_nsxt_security_group.static_group_1.id]
destination_ids = []
action = "ALLOW"
}
}If you are wanting to create multiple rules within a Distributed Firewall, here below I will show some examples – This will not be a part of the code implementation.
##### Sample DFW Rule Creation
resource "vcd_nsxt_distributed_firewall" "lab-03-pro-dfw-1" {
depends_on = [vcd_org_vdc.demo-org-10]
org = "demo-org-10"
vdc_group_id = vcd_vdc_group.demo-vdc-group.id
rule {
name = "rule-1" # Here you will create your name for the specific firewall rule
direction = "IN_OUT" # One of IN, OUT, or IN_OUT. (default IN_OUT)
ip_protocol = "IPV4"
source_ids = []
destination_ids = []
action = "ALLOW"
}
}Some more detailed information from Terraform site –
Each Firewall Rule contains following attributes:
name– (Required) Explanatory name for firewall rule (uniqueness not enforced)comment– (Optional; VCD 10.3.2+) Comment field shown in UIdescription– (Optional) Description of firewall rule (not shown in UI)direction– (Optional) One ofIN,OUT, orIN_OUT. (defaultIN_OUT)ip_protocol– (Optional) One ofIPV4,IPV6, orIPV4_IPV6(defaultIPV4_IPV6)action– (Required) Defines if it shouldALLOW,DROP,REJECTtraffic.REJECTis only supported in VCD 10.2.2+enabled– (Optional) Defines if the rule is enabled (defaulttrue)logging– (Optional) Defines if logging for this rule is enabled (defaultfalse)source_ids– (Optional) A set of source object Firewall Groups (IP SetsorSecurity groups). Leaving it empty matchesAny(all)destination_ids– (Optional) A set of source object Firewall Groups (IP SetsorSecurity groups). Leaving it empty matchesAny(all)app_port_profile_ids– (Optional) An optional set of Application Port Profiles.network_context_profile_ids– (Optional) An optional set of Network Context Profiles. Can be looked up usingvcd_nsxt_network_context_profiledata source.source_groups_excluded– (Optional; VCD 10.3.2+) – reverses value ofsource_idsfor the rule to match everything except specified IDs.destination_groups_excluded– (Optional; VCD 10.3.2+) – reverses value ofdestination_idsfor the rule to match everything except specified IDs.
Now that we have established firewall rules within our template, next you can IP Sets which are kind of a Group that you can use for ACL’s and integrate them into a firewall and static groups etc!
#### Demo Org 10 IP sets
resource "vcd_nsxt_ip_set" "ipset-server-1" {
org = "demo-org-10" # Optional
edge_gateway_id = vcd_nsxt_edgegateway.lab-03-pro-gw-01.id
name = "first-ip-set"
description = "IP Set containing IPv4 address for a server"
ip_addresses = [
"10.10.10.50",
]
}Static Groups are another great way to assign networks and members. For this example, my Static Group consists of my domain network segment and with this I can utilize the group into firewall rules.
#### Create Static Group
resource "vcd_nsxt_security_group" "static_group_1" {
org = "demo-org-10"
edge_gateway_id = vcd_nsxt_edgegateway.lab-03-pro-gw-01.id
name = "domain-network"
description = "Security Group containing domain network"
member_org_network_ids = [vcd_network_routed_v2.nsxt-backed-2.id]
}
###########################################################
An example of how to use a Static Group within a firewall rule.
rule {
name = "domain-network" ## firewall rule name
action = "ALLOW"
direction = "IN_OUT"
ip_protocol = "IPV4"
source_ids = [vcd_nsxt_security_group.sg-domain-network.id]
destination_ids = [vcd_nsxt_security_group.sg-domain-network.id]
logging = true
}That is it for the automation for Part 2 of VMware Cloud Director! Stay Tuned for more automation!